“Standards should not be forced down from above but rather set by the production workers themselves”
Taiichi Ohno
Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management with Supply Chain 4.0
A supply chain 4.0 contains all the businesses & individual contributors involved in developing a product, from raw materials to completed merchandise. Moreover, At the center of all supply chain management topics are the physical flows of materials & goods, which have to be designed in value creation networks in such a manner that they provide us customers with the best viable benefit. So, The concept of the supply “chain” comes from military ideas of how supply moves from one point to the other in a sequential order where each point is connected.
Digital Supply Chain or supply chain 4.0 is key to the operations of each organization that manufactures or distributes anything. Supply Chain 4.0 transformation– the application of the Internet of Things & advanced analytics of big data, the utility of advanced robotics in supply chain management: place sensors in everything, create networks everywhere, automate anything & evaluate everything to notably enhance overall performance & customer satisfaction.
History Of Supply Chain 4.0
Supply chains historically are linear, with a distinct development of layout, source, plan, make and deliver. But, now Supply chain has gone through an immense change. Today, supply chains are changing from a quiet sequence to a dynamic, interconnected system. Further, This switch from linear, straight supply chain operations to an interconnected, open system of supply operations could lay the basis for how businesses compete in the future.
Traditionally, supply chain professionals controlled the “four Vs” (volatility, velocity, volume & visibility) as they tried to optimize effects throughout a sequence of goals that consist of the total cost, quality, service & support for innovation. These traditional priorities are not likely to change, however moving forward, supply chain decision-makers ought to be capable to attain higher levels of overall performance with supply chain capabilities evolved with new digital technologies in digital transformation.
Digitization creates a disruption & needs companies to reconsider the manner they layout their supply chain. At the same time, consumer expectations are growing recent online trends have brought about expanding service expectations integrated with much more detailed orders. Thus, The online-enabled transparency & easy access to a lot of options concerning where to shop & what to buy drive the competition of supply chains.
Change is frequently hard, however, the digitization of information & the utility of advanced innovative technologies presents the possibilities to drive business value throughout the supply chain. Moreover, digital disruption can alternate supply chains in any industry of VUCA environment.
Handpicked for you: Supply Chain Transformation Strategy
Supply Chain 4.0 Process
The supply chain transformation may be deployed to play an important role in making sure positive consumer experiences. Now, organizations are combining the digital supply chain throughout historically siloed business areas that comprise manufacturing, logistics, supply chain planning & aftersales service, and maintenance.
The purpose is to connect everything digitally to ideal operational reality as much as possible.
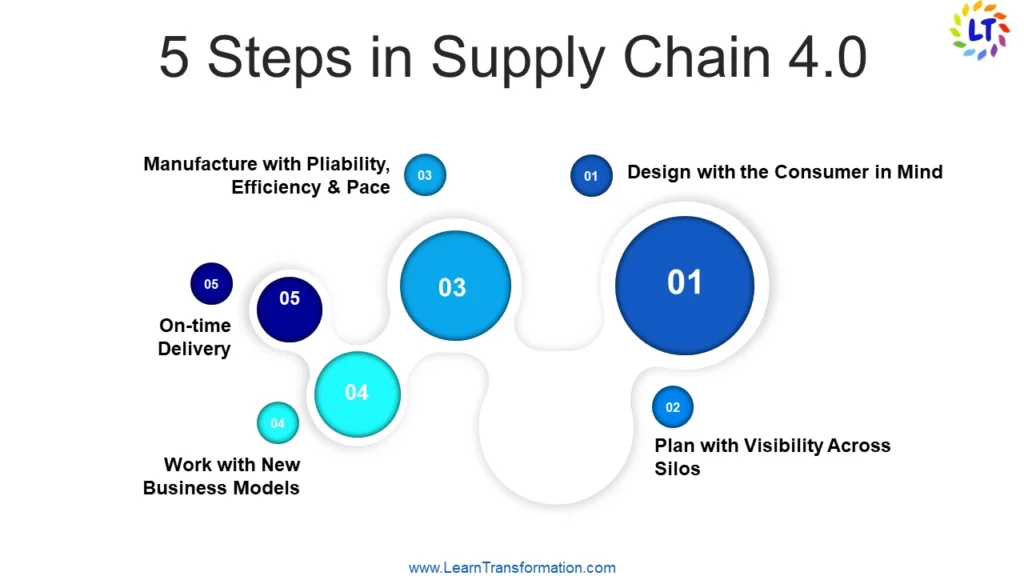
1. Supply chain 4.0 first step-Design with the Consumer in Mind
In the design phase, organizations require this level of connection to inspect trends and innovate in the direction consumers want. Progressively, organizations want to design smarter, Industry 4.0 enabled products & assets that have built-in sensors to capture real-time data once they are in use in a live environment. It’s additionally vital to assume in terms of compliant product lifecycle management – it calls for product development to involve in the supply chain from the start for effective implementation of business transformation.
2. Supply chain 4.0-second step-Plan with Visibility Across Silos
To be more responsive & decrease the time of planning cycles, organizations require to connect across departmental silos for a joint view of real-time supply & demand that helps balance inventory and service levels. To pace making plan cycles & react quickly to change, planners need synchronized planning processes that ruin down silos & tools to swiftly run simulations for higher decision-making in lean transformation.
3. Manufacture with Pliability, Efficiency & Pace
When it appears to manufacture, advanced digital supply chain 4.0 capabilities & higher interactions can help organizations amplify shop floor visibility, identify process congestions & control operations with sharpness. Further, This, in return, eases smart factory abilities where hard production lines are converted into flexible manufacturing cells – making it feasible to switch from mass production to mass customization.
4. On-time Delivery
The delivery phase is a vital component of the supply chain that can make or ruin the consumer experience. Connected vehicles, for instance, can optimize transport routes primarily based on real-time climate & traffic conditions, support real-time tracking, and monitor conditions such as the temperature in freezer compartments. New technology leverages robots & augmented reality to assist staff, amplify productivity & deliver the products to consumers quicker.
5. Work with New Business Models
Finally, many organizations are modifying the working phase with IoT-connected assets that plug straight into the digital trends for supply chain 4.0. This allows drive, new business models, wherein the manufacturer owns the asset & charges the customer for usage, uptime, or some other metric.
Leader’s Tip:
To enable real-time data transmission and collaboration, embrace cutting-edge technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing.
Future Insights of Digital Supply Chain or Supply Chain 4.0
Efficiency:
Efficiency in the supply chain 4.0 is amplified by the automation of both physical activities & planning. Robots manage the material fully automatically alongside the warehouse process – from receiving to putting away to pick, pack & deliver. Autonomous trucks ship the goods in the network. To optimize truck utilization & increase transport flexibility, Companies apply cross-company transport optimization to share capacities between companies.
Granular:
The customers’ demand for individualized products is consistently amplifying. That gives a strong hit towards micro-segmentation & huge personalization ideas will ultimately fulfill. Moreover, Consumers are much more granular clusters & a wide spectrum of products they want will offer. Further, This allows customers to choose one of the multiple “logistics menus” that perfectly suits their requirements. New transport concepts, such as drone delivery, permit companies to control the last milestone effectively for single & high-value dense packages.
Quicker:
New approaches to product distribution decrease the delivery time. The advanced predicting approaches develop the basis of these services. For instance, predictive analytics of internal (e.g., demand) & external (e.g., market trends, weather, construction indices) data, and provides a much more accurate prediction of customer demand. Moreover, Prediction of weekly and for the very trending products even every day. In the future, we can see “predictive shipping,” for which Amazon grips a patent – products are shipped earlier than the consumer places an order. The customer order is in a while matched with a shipment that is already being shipped towards the customer region. And the shipment is rerouted to the proper client destination.
Flexible:
New business models, such as Supply Chain 4.0 as a Service for supply chain planning functions or transport management. This amplifies the flexibility within the supply chain organization. The supply chain can be bought as a service & paid for on a by-usage basis rather than having the resources & capabilities in-house.
Best Video for you:
Amplifying Operational Efficiency by leveraging Supply Chain 4.0
Supply Chain 4.0 has an impact on all regions of supply-chain management. This is apparent within side the way the primary Supply Chain 4.0 capability improvement levers are shown in the outer circle map to six main value drivers (the inner circle).
1. Planning
Supply-chain 4.0 planning will benefit extremely from big data & advanced analytics, also from the automation of knowledge work. Some consumer goods players are already using predictive analytics in demand planning to evaluate hundreds to thousands of internal & external demands. The influencing variables (e.g., climate, traits from social networks, sensor data). The use of machine-learning techniques to model complex relationships and derive a precise demand plan. Predicting errors often fall by 30 to 50 %.
Heavily automated, fully integrated demand & supply planning breaks traditional boundaries between the various planning steps. It modifies planning into a flexible, consistent process.
2. Physical Flow
Logistics will take a big step forward through better connectivity, additive manufacturing, advanced analytics & advanced automation. Unceasing traditional warehousing & inventory-management strategies for enabling better digital transformation. Easy-to-use interfaces such as wearables already provide location-based instructions to employees, guiding picking processes.
Autonomous & smart vehicles will lead to a notable operating-cost reduction in transportation & product handling. While at the same time decreasing lead times & environmental costs. Linking warehouses to production loading points additionally even allows complete processes to be performed with effective minimum guide intervention. Finally, as production facilities begin to depend extra on 3-D printing, the role of the warehouse may alternate basically.
3. Performance Management
Performance management also is modified extremely. With various big food companies taking a lead in making detailed, consistently updated, easily personalized dashboards available throughout their organization transformation. Those days are gone, when generating dashboards was a big task & performance indicator were available only at summation levels. Performance management is now turning into a truly operational process equipped with real-time exception handling & continuous improvement. Rather than a retrospective exercise on a monthly or quarterly basis.
4. Order Management
A couple of measures enhances order management: no-contact order processing combines the ordering system to the available-to-promise (ATP) process, and real-time remodeling enables order-date confirmations through immediate, in-memory redeveloping of the production schedule and replenishment needs in consideration of all constraints. The final result is decreased costs, improved reliability, and better customer experience, eventually leading to a better transformation.
5. Collaboration
The supply-chain cloud makes the following chain of collaboration in the supply chain. Supply-chain clouds are unified supply-chain platforms among customers. The company & suppliers, offering a shared logistics infrastructure or even joint planning solutions. Especially in noncompetitive relationships, partners can decide to handle supply-chain tasks together to save administrative costs & learn from each other.
It additionally slashes lead times, way to immediate information provision for the duration of the whole chain. While providing an early-warning system & the capacity to react quickly to disruptions anywhere.
6. Supply-chain Strategy
Following the want for further individualization & customization of the supply chain. 4.0, supply-chain 4.0 trends undertake many more segments. To excel in this setting, supply chains require to grasp micro-segmentation. The big data approach allows for the huge customization of supply-chain offerings. It does it by keeping apart the supply chain into hundreds of individual supply-chain transformation segments, each primarily based on consumer desires & the company’s capabilities. Customized products offer optimal value for the customer & help minimize costs and inventory in the supply chain.
Leader’s Tip:
To acquire practical insights and make data-driven decisions for supply chain optimisation, invest in data analytics capabilities.
Final Word
The possible impact of Supply Chain 4.0 in the following 2-3 years is going to be enormous. Up to 30 percent decreased operational costs and a deduction of 75 percent in lost sales. While lessening inventories by up to 75 percent are anticipated, at the same time improving the agility of the supply chains considerably.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 stages of Supply Chain?
organizations are combining the digital supply chain throughout historically siloed business areas that comprise manufacturing, logistics, supply chain planning & aftersales service, and maintenance.
Stages are:
- Design with the Consumer in Mind,
- Plan with Visibility Across Silos,
- Manufacture with Pliability,
- Efficiency & Pace,
- On-time Delivery,
- Work with New Business Models
What is Supply Chain 4.0 all about?
Supply Chain 4.0 transformation– the application of the Internet of Things & advanced analytics of big data, the utility of advanced robotics in supply chain management: place sensors in everything, create networks everywhere, automate anything & evaluate everything to notably enhance overall performance & customer satisfaction.
What are the benefits of Supply Chain 4.0?
Some of the benefits of Supply Chain 4.0 include increased efficiency, improved visibility, enhanced collaboration, reduced costs, and greater agility and responsiveness to customer needs
What are some key technologies driving Supply Chain 4.0?
Some key technologies driving Supply Chain 4.0 include the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotic process automation (RPA).
How can organizations prepare for Supply Chain 4.0?
Organizations can prepare for Supply Chain 4.0 by developing a clear strategy, investing in the right technology and talent, collaborating with partners, and measuring and monitoring performance.
What are some potential challenges of implementing Supply Chain 4.0?
Some potential challenges of implementing Supply Chain 4.0 include the complexity of integrating different technologies, the need for new skills and talent, the risk of cyber-security threats, and the challenge of managing large amounts of data.
Key Takeaways
- End-to-end visibility, transparency, and traceability of goods and procedures in the supply chain are made possible through digitalization.
- Operations are streamlined, efficiency is increased, and human error is decreased in supply chain activities thanks to automation and robotics.
- When it comes to adjusting to market dynamics, changes in demand, and disruptions, agility is essential since it promotes resilience and competitive advantage.

