Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day-in and day-out.
Robert Collier
Understanding Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
Quality Control and Assurance is another approach whose use is increasing day by day that helps your organization to transform into a better one. It will also help your organization to build successfully by maintaining a standard of product delivery and customer expectations. If you want to eliminate waste. Then. To attain a higher level of productivity, and make your business efficient. You should read this article which will make you aware of the meaning of Quality Assurance and Quality Control and its benefits.
Before we take a look at Quality Assurance vs Quality Control, let’s get to know what these two terms mean.
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance is a way of averting errors and defects present in manufactured products. It also refers to the avoidance of problems while delivering products and services to consumers. Furthermore, we can also interpret it as a crucial part of quality management that focuses on giving confidence that the requirements in product quality will fulfill. This confidence provided through “Quality Assurance” internally affects the management of an organization. Whereas externally affects the customers, government agencies, third parties, etc. By ensuring “Quality Assurance” in an organization, the final product’s standard is observed. Moreover, it also helps in the development and implementation of inspection activities, detection of problems, and delivery of reasonable outcomes.
Must Read: Best Books
What is Quality Control?
This term is more like a process in which the quality of all factors that includes in the production process. Like “Quality Assurance”, “Quality Control” is also a part of management. It is concentrated on fulfilling the quality requirements of a product. Through this process, an organization can ensure that the quality of the product is maintained and improved. Usually, it involves the testing of units and determining whether they are under the specifications or not. We can also define it as the set of actions that helps in controlling the quality of the product by detecting any bugs if present.
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
Both the terms, Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC), are used interchangeably. Now, that you’ve got an overview of both the terms, let’s take a look at the points of difference between them.
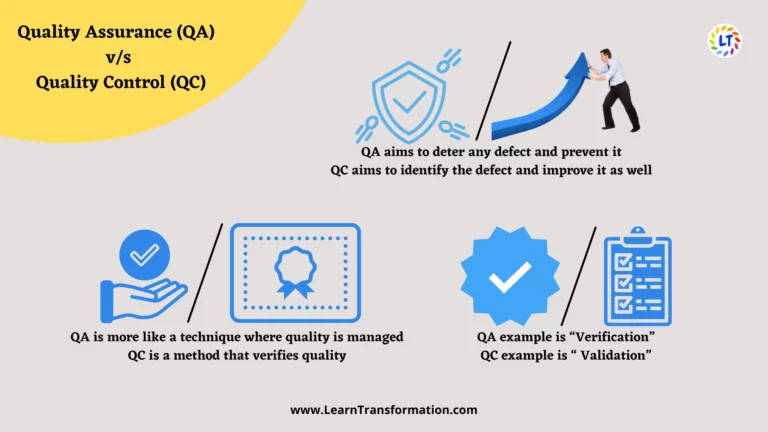
- QA is a process that focuses on assuring that the request about the product’s quality. Whereas, QC is the process that concentrates on the fulfillment of the quality request.
- QA aims to deter any defect and prevent it. Whereas, QC aims to identify the defect and improve it as well.
- QA is more like a technique where quality is managed, whereas, QC is a method that verifies quality.
- QA doesn’t demand the execution of programs, whereas, QC requires the execution of programs.
- QA is assured by all team members, whereas, only the testing team is credible for QC.
- QA’s statistical technique is known as Statistical Process Control, whereas, the statistical method used in QC is Statistical Quality Control.
- QA helps you to be sure that you are doing the right thing. Whereas, QC makes sure that the results of what you did are up to your expectations.
- QA clarifies the principles and methodologies that needs to follow to meet the customer’s requirements. Whereas, QC makes sure that the standards should follow along with working on the product.
- The process of QA creates the deliverables, whereas, the process of QC verifies those deliverables.
- A QA example is “Verification”, whereas, a QC example is “ Validation”.
Also Read: Mentoring vs Coaching: 10 Key Differences and Benefits
Leader’s Tip:
Establish solid procedures and standards to prevent errors and advance continuous improvement to encourage a proactive approach to quality assurance.
Check out the Video-
What are the 7 Quality Control (QC) tools?
Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese professor of engineering created these 7 QC Tools. The goal was the implementation of basic and user-friendly tools that the employees from each background with varied skills could use without any such requirement of extensive training. Later on, these 7 tools implement in Japan’s industrial training program that was during the country’s postwar period. The usage of those 7 tools turned into statistical quality control as a means of quality assurance. Still today, these tools that help in quality management. And, we consider the gold standard for managing a variety of quality-related issues. These tools execute along with some of the widely used process improvement methodologies like Six Sigma, Lean Management, etc. Let’s take a glance at those 7 QC tools-
1. Stratification
The stratification analysis tool is a quality assurance tool that we use to sort data, objects, and people as well into distinct groups. If you segregate your data by using this tool, then you will be able to determine its meaning or reveal some patterns that wouldn’t have been notified otherwise. Stratified analysis of your data allows you to make sense of your data previously, during, and after its collection. To receive the most out of this tool, you should always consider which type of information about your data sources can possibly affect the results of your data analysis. Moreover, you should make sure that your data set up in such a way that all the necessary information is in it.
2. Histogram
Often, the quality specialists allocates with the work of analyzing and interpreting the different groups of data’s behavior to manage and maintain quality. This is where another QC tool, Histogram comes into action. This particular tool helps you to exemplify the distribution of data clearly. It has a structure identical to the bar graph, Where each bar represents a group. Whereas, the height of the bar graph represents the frequency of data within that group. This tool helps in breaking down the frequency of your data into categories such as age, days, physical measurements, etc.
3. Check Sheet or Tally Sheet
Check Sheets are for the collection of qualitative and quantitative data. While collecting quantitative data, we can call this tool a Tally sheet. Whereas, a Check sheet collects data in the form of checkmarks that helps to indicate how many times a specific value has occurred. This ultimately helps you to quickly zero the flaws within your process, defect patterns, and also causes of some particular defects. As it has a simple setup and graphics that are simple to understand, this tool makes it easy to record the preliminary frequency distribution of data.
4. Cause and Effect Diagram
Also known as the Fishbone diagram, it is a QC tool that operates by defining an issue related to quality on the right-hand side of the diagram. We can group this tool’s causes and sub-causes mainly into these six groups, measurements, personnel, environment, machines, and methods. These groups help in the identification of the likely source of your problem, while also keeping the diagram structure.
5. Pareto Chart (80-20 Rule)
The Pareto Chart utilizes the 80-20 rule, where it is assumed that in any process, it’s 80% of problems are caused by 20% of the major factor, whereas, 20% of problems are risen by 80% of minor elements. The Pareto chart is a combination of a bar and a line graph, that portrays the individual values in descending order. This tool aims to highlight the significance of various parameters, which allows you to identify and direct your efforts on such factors that affect the part of the process.
6. Scatter Diagram
This tool is most helpful in illustrating the relationship between two variables and it is suitable for QA professionals. Each dot at the Y-axis (dependent value) and X-axis (independent value) represents a common intersection point. When we assemble these points, they depict the relationship between variables. A stronger correlation in your diagram will assure an even stronger relationship between variables.
7. Control Chart
Also called the Shewhart chart, this tool helps the experts to determine whether a process is predictable or not, which helps you to recognize factors that may lead to any sort of variations. These charts use a central line that depicts upper and lower control limits that are based on historical data. Using this chart will save your organization time and money by foreseeing the performance of a process.
Leader’s Tip:
QA and QC teams should work together to ensure effective communication and shared accountability for quality outcomes.
Conclusion
Thus, hereby we can conclude that both Quality Assurance and Quality Control are significant parts of quality management. The QA process reviews the management uses quality plan to make vital decisions on the improvement of the processes. While the QC process verifies that quality standard quality is executed to the process and uses it frequently to accept or reject products. Despite their differences, they work as two critical components in a quality management program. QA and QC function together to assure the ongoing quality of end products along with gaining the satisfaction and confidence of the customers. QA’s and QC’s altogether implementation results in the success of the organization. Lastly, the 7 tools of QC are also vital as they increase the product and process quality adequately.
FAQs
Why is Quality Assurance (QA) considered a proactive process?
QA is considered proactive because it focuses on preventing defects and issues from occurring in the first place. It involves establishing processes, standards, and guidelines to ensure that quality requirements are met consistently. By implementing preventive measures and conducting regular audits, QA aims to identify potential problems early on and address them before they become significant issues.
How does Quality Control (QC) differ from Quality Assurance (QA) in terms of timing?
QA activities are performed throughout the development or production process, whereas QC activities typically occur at the end of the process or during specific checkpoints. QA focuses on preventing defects and ensuring quality at every stage, while QC involves inspecting and testing the final product or service to identify any existing defects.
Key Takeaways
- While QC entails finding and correcting flaws in the finished product or service, QA is more concerned with preventing flaws through proactive measures.
- The 7 QC Tools, which include histograms and check sheets, support quality control by gathering and analysing data to facilitate wise decision-making.
- In order to achieve and maintain high-quality products or services through prevention and detection procedures, QA and QC are complementary processes.