“A good objective of leadership is to help those who are doing poorly to do well and to help those who are doing well to do even better.”
-Jim Rohn
Transform Your Organization with Lean Principles
Lean methodologies are lean since they empower a business to accomplish more with less. A lean association utilizes less human effort, less equipment, less office space, less time, and less capital- while continually coming nearer to meeting clients’ accurate necessities. Lean principles is the protection of important assets than it is about cost-cutting.
Therefore, Thusly, lean isn’t simply one more cost-cutting system of the sort we frequently find in business associations.
Also Read: Best Books
Learning Objectives
- Know what is implied by lean controls, and why the subject can be confounding.
- Understand the utilization of lean.
- Know the five principles of lean.
Handpicked for our Leaders: 5 Challenges and Role of a Good Leader
- Lean control, or essentially lean, has become an enormously well-known business control and improvement approach lately. Lean control is a profoundly refine case of nonfinancial controls in action.
- Lean is an arrangement of nonfinancial controls that we use to improve item and administration quality and decrease waste. Further, The research recommends that up to 70% of assembling firms are utilizing some type of lean in their business tasks.
- Lean was initially centered around improving assembling activities, yet is currently used to improve product advancement, order preparation, and a variety of other non-manufacturing processes (some of the time called “lean in the office“).
Leader’s Tip:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to identify and eliminate waste in their processes.
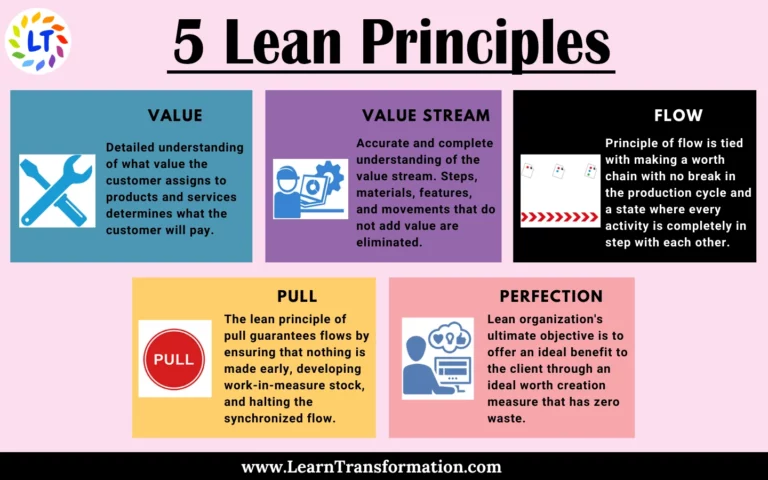
5 Lean Principles that You should Know

Every one of the five lean principles of Lean thinking expands on one another and afterward, start again to make a consistent pattern of progress. So, Those 5 keys lean principles are:
- Value
- Value stream
- Flow
- Pull
- Perfection
1. The Value Lean Principle
The Lean approach begins with a detailed understanding of what value the customer assigns to products and services. Moreover, This is what determines what the customer will pay. Furthermore, Establishing value permits associations to make a top-down target cost. The expense to produce the items and services is then decided. The organization focuses on eliminating waste so that it can deliver the value, the customer expects at the highest level of profitability.
2. The Value Stream Lean Principle
The value stream is the totality of the product’s entire lifecycle from the raw materials through to the customer’s use of, and eventual disposal of, the product. In order to eliminate waste, the ultimate goal of Lean, there must be an accurate and complete understanding of the value stream. Steps, materials, features, as well as movements are eliminated as they don’t add value . Value stream mapping will almost always reveal 3 types of Muda. (Muda is Japanese for waste).
- Many steps will be found to unambiguously create value.
- Many other steps will be found to create no value but to be unavoidable with current technologies and production assets.
Check out the Video-
3. The Flow Lean Principle
Understanding flow is essential to the elimination of waste. So, The lean manufacturing principle of flow is tied in with making a worth chain with no break in the production cycle and a state where every activity is completely in step with each other.
4. The Pull Lean Principle
The lean principle of pull guarantees flows by ensuring that nothing is produce early, developing work-in-measure stock, and halting the synchronized flow. Rather than using the traditional American manufacturing approach of pushing the work through based on a forecast and schedule, the pull approach dictates that nothing is produce until the customer orders it. Moreover, This requires a lot of adaptability and a short design to deliver process durations. It also requires an efficient way of communicating what is in need for each step in the value chain.
Handpicked for our Leaders: Lean in Non-Manufacturing
5. The Perfection Lean Principle
Lean practitioner’s endeavor to achieve nothing short of perfection. Further, The march toward a wonderful cycle happens step by step as constant improvement address the main causes of quality problems and production waste.
The relentless pursuit of perfection is what drives users of the approach to dig deeper, measure more, and change more often than their competitors.
A lean organization understands the client value and focuses its key processes to continuously build it. An ultimate objective is to offer an ideal benefit to the client through an ideal worth creation measure that has zero waste.
Leader’s Tip:
Utilize frontline employees’ knowledge and insights to generate significant change by empowering and including them in decision-making.
Conclusion
At last, Lean transformation highly recommends that you pick up a copy of Lean Thinking, which goes into far greater depth about each of these principles of Lean manufacturing. It additionally offers insightful and unexpected examples across almost every industry. These thoughts structure the establishment of the Lean approach that has changed incalculable corporations, giving them a leg on the opposition and a make way to both productivity and delighted clients.
FAQ’s
What are the 5 main principles of lean Organisation techniques?
5 keys lean principles are:
- Value
- Value stream
- Flow
- Pull
- Perfection
What is the most important lean principle?
Every one of the five principles of Lean thinking expands on one another and afterward, start again to make a consistent pattern of progress. Those 5 keys lean principles are: Value , Value stream, Flow , Pull , Perfection.
Key Takeaways
- Concentrate on providing value to clients and stop doing things that don’t make them happy.
- To reduce errors and boost productivity, stress the value of regular procedures and work towards uniformity.
- Promote a culture of experimentation and learning where failures are viewed as chances for improvement and creativity.