Nature does constant value stream mapping, it’s called evolution.
Carrie Latest.
Lean Six Sigma is a data-controlled perspective to enhance efficiency, profits & customer satisfaction. Lean Six Sigma is a strong tool. Over the past few decades, companies universally have saved numberless millions by including Lean & Six Sigma principles into their processes. Further, It has been applied progressively across various industries. Moreover, Telecommunications, Information technology, sales, healthcare, finance & even the military have used Lean Six Sigma to modify processes– regularly proving the important thing to anticipate in today’s busy marketplace.
Unlock a world of knowledge with just one click: Navigating Lean Digital Transformation
Lean Six Sigma is the union of two popular process Improvement methods, Lean and Six Sigma, which can be combined to shape a strong tool to enhance enterprise processes. In addition to this, Lean Six Sigma provides an organized approach to help employees build their problem-solving skills. Further, It helps in “seeking a better way” which becomes a regular habit.
Before jumping into details, it’s essential to filter the concept of process improvement. Since Lean Six Sigma is a system for inspecting & improving processes. So, Let’s understand those terms first.
Process: A process is a sequence of steps engaged in developing a product or delivering a service. Further, Nearly everything we do is a process— manufacturing a laptop, baking a cake, or treating a cancer patient.
Process Improvement: Process improvement needs employees to better understand the present state of how a process functions to eliminate the blockades to serving customers. Since each product or service is the outcome of a process, gaining the skills needed to remove waste, rework or inefficiency is critical for the growth of an organization.
How Lean Six Sigma Originated?
Lean originated at Toyota in the mid of 20th century & Six Sigma originated at Motorola in the ’80s. Although they’ve been taught as separate methods for many years, the line has obscured & it’s now common to see Lean & Six Sigma teachings united to gain the best of both worlds. By joining these methods, you have the best shot at applying the right mindset, techniques & tools to solve the problem.
What is Lean?
Lean refers to eliminating or reducing waste in your business. Waste is anything that doesn’t add any value to your organization. Mostly we have 8 types of waste, which is also famous as DOWNTIME. So, Waste applies to every industry & sector, from defense to hospitality. Thus, By eliminating the waste, it becomes possible for lean principles to only produce the right material, in the right quantity wished by the customer, at exactly the right time.
This results in a process that is more efficient & delivers products to the customer more swiftly. Lean depends on people to identify what problems are causing waste. Learn tools for process improvement include the kanban inventory control cues, 5 whys, Ishikawa fishbone diagrams, takt time calculations & value stream mapping.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a popular quality improvement methodology made popular by General Electronics & Motorola. Lean Six Sigma principles focuses on reducing the variation within a process. There are several reasons for variation in a process. Examples include different operators, machine/tool wear, fatigue, different raw materials, different equipment, environmental changes (humidity, temperature, light, etc). Straightly for any organization to reap Six Sigma, it can’t generate more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
This is attained by using careful measurement & utilizing project management tools such as stochastic optimization, statistical analysis to understand which ‘levers’ to pull to generate the desired result. Its tools are designed to be utilized by a selective quantity of personnel who have been selected to get hold of formal training in progressive levels of study. Management strategies include DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) and DMADV (define, measure, analyze, design, verify), both of which are based on Deming’s plan-do-check-act cycle.
Six Sigma relies on information to perceive problems in an enterprise process. Where a lean event might only last for a week, a typical six sigma project can typically last for up to 6 months.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that looks to unite the best of both the lean & the Six Sigma approaches for lean transformation in an organization. Further, Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-controlled method of development that values defect prevention over defect detection. It drives consumer satisfaction & outcomes by reducing waste, variation & cycle time, while promoting the utilization of work standardization & flow, so creating a competitive advantage.
Lean Six Sigma course applies anywhere variation & waste exist. Additionally, Lean manufacturing highlights streamlining business processes, Six Sigma focuses on removing defects in these processes. Further, Six Sigma teams are seeking to eliminate defects in enterprise processes with the aid of using minimizing variation within the processes. Teaching Lean principles initially to obtain momentum, then introducing the Six Sigma process in a while to address the extra advanced problems. So, particularly the emphasis is on attaining the benefits of both methodologies while minimizing any possible weaknesses.
For instance, trying to take advantage of the velocity inherent in the lean method, while maintaining the statistical rigor of the Six Sigma style. Using an amalgam of both approaches also opens up the number of tools & techniques available to solve any particular problem.
Check out the Video:
What are the Benefits of Lean Six Sigma?
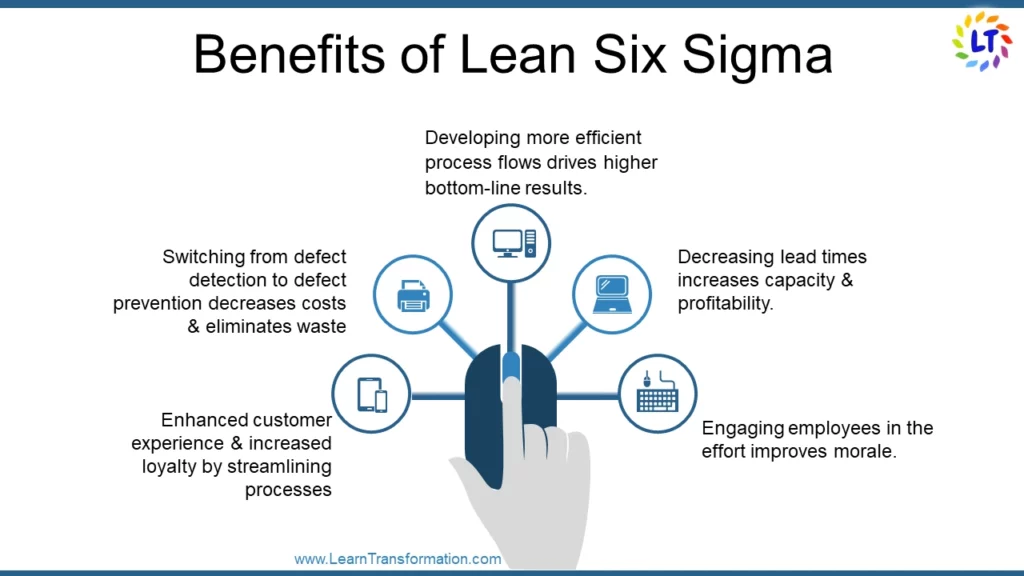
- Switching from defect detection to defect prevention decreases costs as well as eliminates waste.
- Enhanced customer experience & increased loyalty by streamlining processes.
- Developing more efficient process flows drives higher bottom-line results.
- Decreasing lead times increases capacity as well as profitability.
- Engaging employees in the effort improves morale.
About Lean Six Sigma Certifications
We can achieve Lean Six Sigma certification at differing levels based on the training an individual has obtained. Its certification levels are also split into various belts.
Leader’s Tip
To effectively implement Lean Six Sigma projects, cultivate a culture of data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Six Sigma white belt is the first level of Lean Six Sigma certification. The white belt aims to provide trainees with a basic understanding of Lean Six Sigma methodology, comprising but not restricted to process improvement, variability, removing negative effects on process performance & deciding what roles particular team members should play.
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow belt is the next in the Lean Six Sigma certification. Furthermore, The yellow belt begins the training from the white belt certification course and aims to give trainees a more detailed & broad understanding of Lean Six Sigma methodologies.
- Lean Six Sigma Green belt is the 3rd step in the Lean Six Sigma training process, following the six-sigma yellow belt. Moreover, The six sigma green belt concentrates on the application of the Lean Six Sigma methodologies defined in the white and yellow belt courses. In green belt training courses, trainees learn to chart & plan the roles of individuals within Lean Six Sigma teams, additionally learning how to run statistical tests that are used to improve processes.
- Lean Six Sigma Black belt is the final belt that is given out in the Lean Six Sigma certification process. So, The Lean Six Sigma black belt lessons trainee’s various regression, determine size calculations for experiments, perform factorial experiments & describe various types of process optimization. In a nutshell, the six-sigma black belt is the peak of Lean Six Sigma training.
Also See- Six Sigma Belts: Still impactful in Transforming world?
What are Lean Six Sigma Strategies?
1. Takt Time
Takt Time refers to the speed at which a completed product is finished to fulfill consumer demand. It is an important tool to find if goods flowing from each station to the next in an efficient manner. So, Takt Time provides you the means to measure processes to make sure continuous flow & the optimum utilization of machines and processes.
How to calculate Takt Time?
Mathematically we calculate takt time as follows:
Takt time= Time Available/ Demand
The time available for production should highlight the number of time employees spends operating on the product, subtracting variables Which includes conference breaks & different associated activities. So, Customer demand is determining what number of products a buyer expects to buy.
Both of these variables ought to be steady over an identical time frame, like 1 day or a week. Takt Time isn’t the number of man-hours put into developing a product. Moreover, It refers to the complete period to create a product, from start to finish, ensuring that continuous flow is achieved & customer demand is satisfied.
For Example:
- Total Time: 8 Hours X 60 Minutes = 480 Minutes
- Breaks: 50 Minutes
- Time Available: 430 Minutes
- Customer Demand in 8 Hours: 100 units
- Takt Time: 430 / 100 = 4.3 Minutes = 258 Seconds
In this example, the customer will need 1 unit every 258 seconds. However, you might like to produce a single unit in a little less than 258 seconds to aid any variation in process steps, before implementing takt, it is essential to ensure that your processes are reliable & can deliver good quality.
2. Kanban Pull System
With a Kanban pull system, a customer process prompts a supplying process to produce a product when it is in need. A pull system refers to JIT (Just in Time) efficiency, where the product meets consumer demand, not exceeds it. With a pull system you will have an easier time responding to market forces, but it is mainly about making what the consumer wants when they want it. Alternatively, Kanban describes the signals used inside a pull device through scheduling mixed with travel commands in the shape of visual cards & containers. It enables organization transformation by increasing its efficiency.
Benefits of a Kanban Pull System
- Improved production environment.
- More capital.
- Increased market dynamism.
- Easy monitoring.
3. Five Why’s
The five why’s are an attempted & true method of analyzing & solving a problem. Five why depict the basic cause of an issue. Asking yourself why is important because of the quickest way of getting to the root cause of a problem, flowing through the symptoms & getting right to the basic issues. It is continually a great concept of repeating the five why test while giving alternative answers or asking an employee to conduct the 5 whys for comparison.
For this reason, you can go beyond 5 whys, the key is to stop the exercise when the answers become unserviceable or no more useful responses are given.
4. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
TPM is a team-based system for improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), which includes performance, availability & quality. Further, This aids in developing an approach for growing employee possession autonomously for up keeping the equipment. The goal of the TPM program is to markedly increase production while at the same time amplifying employee morale & job satisfaction.
5. Problem Solving / PDCA / PDSA
The PDCA / PDSA cycle is a 4 phase graphical model for carrying out change at your organization. The method is cyclical, so the PDCA / PDSA cycle should repeated again and again. It is a good idea to use this model at the beginning of a process improvement project, especially for repetitive processes.
- Plan– Find a problem or opportunity & set out a plan for consistent change. Create a hypothesis for what possible issues may be.
- Do– This is the testing phase. This will be a small-scale test where you can easily measure results & obtain a higher understanding of your hypothesis.
- Check– Evaluate if the problem is fixed.
- Act– If the preliminary test was successful, repeat it on a larger scale.
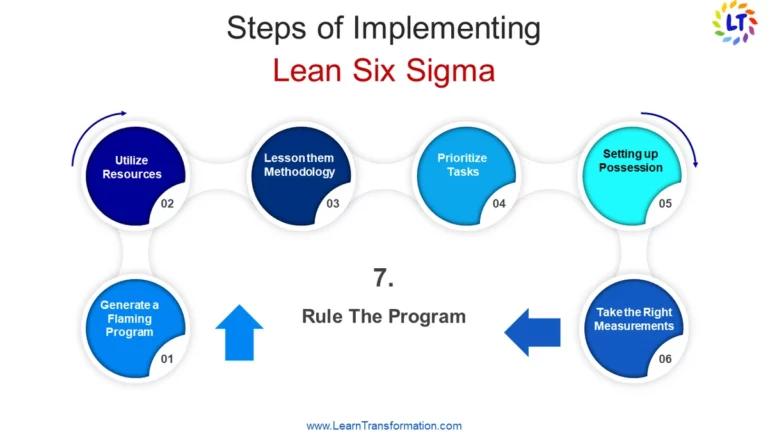
What are Steps of Implementing Lean Six Sigma?
1. Generate a Flaming Program
Organizations must have a captivating reason for implementing Lean Six Sigma. For Instance: You are facing massive quality losses which result in more than 40 % of your costs. Your competitors are attaining your market by 15 % every quarter. Company leadership should be clear with the program and understand how Lean Six Sigma principles can address the problems in the program statement.
2. Utilize Resources
Hire the right resource at the correct price. The resource can be employees, material, or technology. They must be capable to work cooperatively as a team. It is essential to know what to look for in a possible resource. Resources must be able to commit to implementing a shared vision.
3. Lesson them Methodology
If you provide a human with a fish, he can only survive a single day. But if you lesson the person to catch the fish, he can live for a lifetime. For Lean Six Sigma course to survive for a lifetime, businesses require to teach their participants to be robust alternate agents. Six Sigma Yellow belt, Six Sigma Green belt, & Six Sigma Black belt training, along with skilled mentors, can help increase organizational awareness.
Leader’s Tip
Encourage cross-functional cooperation and offer tools and training to develop Lean Six Sigma skills throughout the organisation.
4. Prioritize Tasks
Once resources & training are done, a lot of opportunities may be there. Organizations must make it a priority to:
- Listen to consumer.
- Seeking critical-to-quality standard.
- Make sure Lean Six Sigma efforts are associated with business goals.
It is essential to learn what to miss & where to take risks. Activities must be evaluated to make sure they are meeting the expectations of the organization’s objectives.
5. Setting up Possession
It needs to be apparent who owns the initiative of Lean Six Sigma course. Appoint a committee to seek who is responsible for the complete team. With ownership comes authorization & a sense of pride.
6. Take the Right Measurements
The thing which you can’t measure, you can’t improve it. By generating a measurement system, practitioners can determine baseline performance & utilize the data in decision making & variation analysis. The clue for measurement is to obtain correctly, the quality cost. Organizations also must find a manner to measure process performance to make sure they receive data at a fast speed.
7. Rule the Program
A right governance approach can assist a program to endure strength. Poor governance can lead to the insight falling aside. Proper governance also helps practitioners create a best practice sharing forum. This helps projects to replicate & can highlight common challenges.
Conclusion
The set of methods and tools for developing process, Six Sigma has become a global phenomenon in companies all around the world. Various organizations are using Six Sigma methodologies for improving their operational efficiencies. Also, Lean Transformation Certification is a great way for a leader to improve their leadership capabilities and help the organization and other employees as well.
“4 Best Lean Principles Books”
Global Reader’s Click Below:
- A Factory of One: Applying Lean Principles to Banish Waste and Improve Your Personal Performance
- The 12 Principles of Manufacturing Excellence: A Lean Leader’s Guide to Achieving and Sustaining Excellence, Second Edition
- The Lean Six Sigma Pocket Toolbook: A Quick Reference Guide to 100 Tools for Improving Quality and Speed
- The Lean Turnaround: How Business Leaders Use Lean Principles to Create Value and Transform Their Company
India Reader’s Click below:
- Lean IT – Principles to Practice: Toyota Way to Create Value for the Customer & Wealth for IT Organization
- Creating a Lean R&D System: Lean Principles and Approaches for Pharmaceutical and Research-Based Organizations
- Lean Principles and Application in BPO
- The Principles of Product Development Flow: Second Generation Lean Product Development
FAQs
What is the meaning of Lean 6 Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that looks to unite the best of both the lean & the Six Sigma approaches for lean transformation in an organization. Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-controlled method of development that values defect prevention over defect detection. It drives consumer satisfaction & outcomes by reducing waste, variation & cycle time, while promoting the utilization of work standardization & flow, so creating a competitive advantage.
What is the difference Lean and Six Sigma?
Lean refers to eliminating or reducing waste in your business. Waste is anything that doesn’t add any value to your organization. Mostly we have 8 types of waste, which is also known as DOWNTIME. Six Sigma is a popular quality improvement methodology made popular by General Electronics & Motorola. Straightly for any organization to reap Six Sigma, it can’t generate more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- Lean Six Sigma integrates the concepts of Lean and Six Sigma to minimise waste, increase customer satisfaction, and reduce variance.
- Organisations can achieve operational excellence, improve quality, and promote sustainable performance by embracing Lean Six Sigma.
- Strong leadership backing, thorough data analysis, and an emphasis on customer-centricity are all necessary for the successful adoption of Lean Six Sigma to produce quantifiable results.