Getting the supply chain right is make or break to organizations – particularly in the cutting-edge world, where consumers hope to get goods quicker than ever before.
What is Supply Chain 4.0?
Supply Chain 4.0 – the utilization of the Internet of Things, the utilization of advanced robotics, and the use of advanced analytics of big data in supply chain management. Place sensors in all things, make networks all over, robotize anything, and break down everything to fundamentally improve execution and consumer loyalty.
Over the last 30 years, logistics has gone through a huge change. So, From an absolutely operational capacity that answers to deals or fabricating and zeroed in on guaranteeing. The supply of creation lines and the conveyance to clients, to a free supply chain management work that in certain organizations is as of now drives a CSO – the Chief Supply Chain Officer.
The focal point of the supply chain management work has moved to timely arrangement measures. For example, systematic interest arranging or coordinated S&OP. Which have become set up business measures in numerous organizations, while operational coordination’s has regularly been moved operations to outsider LSPs. So, The supply network work guarantees coordinated activities from clients to suppliers.
Also Read: Digital Supply Chain Transformation: 5 Challenges To Be Successful
What is supply chain?
A supply chain is the whole process of making and selling commercial goods. So, Including each stage from the supply of materials and the assembling of the goods through to their conveyance and deal. Moreover, Effectively overseeing supply chains is basic to any organization planning to compete.
It is a network between an organization and its suppliers to produce and convey a particular product to the final buyer. Further, This network incorporates various exercises, individuals, elements, data, and assets. The supply network likewise speaks to the means. Furthermore, It takes to get the product or service from its original state to the customer. Organizations create it so they can lessen their cost and stay competitive in the business landscape.
A supply chain includes a series of steps required to get an item or service to the customer. Hence, The steps incorporate moving and transforming raw materials into finished items. Moving those items, and distributing them to the end client. So, The entities engaged with it comprises of:
- producers
- Traders
- Stockrooms
- Transportation companies
- Conveyance centres
- Retailers
The components of a supply chain incorporate all the capacities that begin with receiving an order to meet the customer’s requirement. So, These capacities incorporate product development, marketing, undertakings, distribution networks, finance, and customer service.
Also Read: Best Books
Leader’s Tip:
Embrace digital transformation to increase supply chain efficiency and agility by integrating technologies, using data, and promoting cooperation.
See Check out the Video-
Supply Chain 4.0 is that the re-organization of supply chains – design and planning, production, conveyance, utilisation. And, reverse logistics using technologies that we refer as “Industry 4.0”.
These technologies, which emerged within the 21st century, are largely implemented by firms that are at the frontier of supply chain management in high-income countries. However, as we’ll contend, this classification is somewhat artificial, it does. In fact, captures certain prevailing thoughts about what firms got to do, in order to maintain competitive supply networks.
Key differences between Supply chain and Supply chain 4.0
1st difference is:
- A supply chain is a network between an organization and its suppliers to produce and convey a particular item or service.
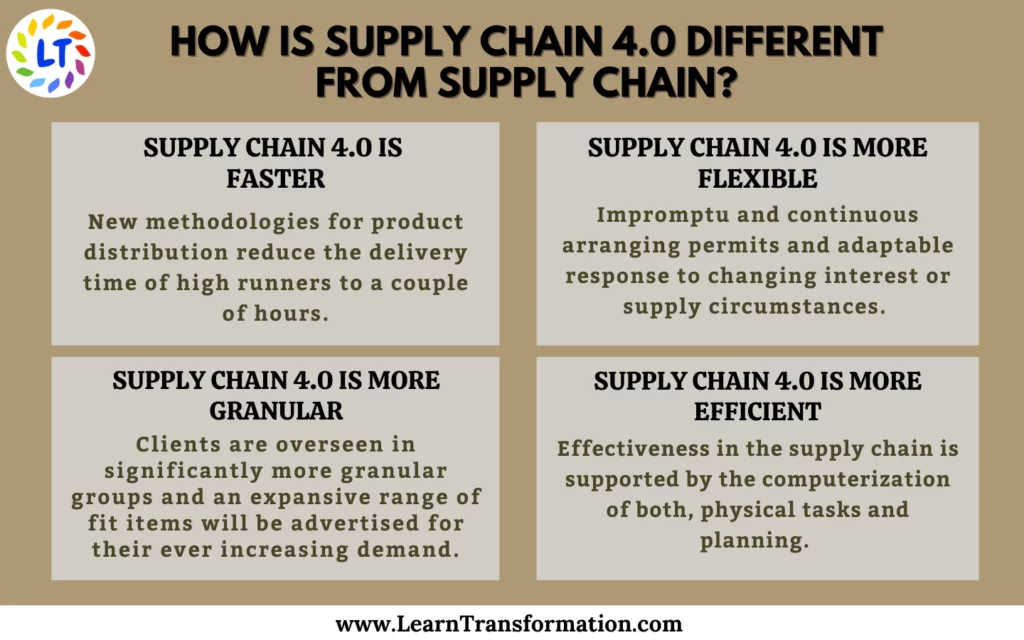
- Supply Chain 4.0 is faster: New methodologies for product distribution reduce the delivery time of high runners to a couple of hours. The basis for these administrations is built by advanced forecasting approaches.
Also Read: The Future of Supply Chain Management in VUCA world
2nd difference is:
- The elements in the supply chain incorporate producers, merchants, stockrooms, transportation organizations, circulation focuses, and retailers.
- Supply Chain 4.0 is more flexible: Impromptu and continuous arranging permits and adaptable response to changing interest or supply circumstances. New plans of action, for example, supply chain as help for supply network arranging capacities or transport management, increment the adaptability in its association. The specialization and focal point of service providers permit them to create economies of scale as well as economies of scope and appealing outsourcing opportunities.
3rd difference is:
- The capacities in a supply chain incorporate product development, marketing, operations, distribution, account, and client support.
- Supply chain 4.0 is more granular: The demand from customers for an ever-increasing number of individualized items is consistently expanding. That gives a solid push towards miniature division, and mass customization thoughts will, at last, be executed. Clients are overseen in significantly more granular groups and an expansive range of fit items will be advertised. Moreover, This empowers clients to choose one of the various ‘coordination’s menus’ that precisely accommodates their needs.
Handpicked for our Leaders: Strong Digital Supply Chain During Supply Chain Transformation
4th difference is:
- Supply chain management brings about lower costs as well as a quicker production cycle.
- Supply chain 4.0 is more efficient: Effectiveness in the supply network is supported by the computerization of both, physical tasks and planning. Robots handle the material (pallets/boxes as well as single pieces) totally naturally along the stockroom cycle. So, From receiving and unloading to putting away to picking, packing, and shipping. Further, The network arrangement itself is persistently improved to guarantee an ideal fit for business prerequisites.
Leader’s Tip:
To ensure the effective adoption of Supply Chain 4.0, invest in people development, change management, and strong cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
So, The transformation into a digital supply chain requires these key points:
- Capabilities and environment: Capabilities regarding digitization need to be built in the organization.
- Implementation of a two-speed organization.
FAQs
What is Supply Chain 4.0?
Supply Chain 4.0 refers to the integration of digital technologies and data-driven capabilities into traditional supply chain management practices. It involves the use of technologies like artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and cloud computing to enhance visibility, agility, and efficiency in the supply chain.
What are the challenges in implementing Supply Chain 4.0?
- Data Security and Privacy: Collecting, analyzing, and sharing large amounts of data require robust security measures to protect sensitive information and comply with privacy regulations.
- Talent and Skill Gap: Organizations need skilled professionals who understand digital technologies and can effectively implement and manage them within the supply chain.
- Legacy System Integration: Integrating new digital technologies with existing legacy systems and infrastructure can be complex and require careful planning and investment.
- Change Management: Shifting to a digital supply chain requires a cultural shift, change management efforts, and stakeholder buy-in to ensure successful adoption and implementation.
Key Takeaways
- For improved productivity and customer experience, supply chain 4.0 places a strong emphasis on connection, data-driven decision making, automation, and customer centricity.
- Adopting Supply Chain 4.0 has advantages such as better visibility, cost savings, greater customer experiences, and higher agility.
- Data security, a talent gap, the integration of legacy systems, change management, and the need for scalability are among the obstacles to Supply Chain 4.0 implementation.