“Calamity is the test of integrity.”
Samuel Richardson
Lean Principles
Toyota principles not only benefits the company but also leads to personal and emotional growth and provides a new way of working to the team. So, Lean principles gives new shades to leadership and creates sustainable business success.
Principles That Every Leader Should know
Lean production aims to eliminate waste, or any process’ non-value-added components. A process retains some waste unless it has been lean numerous times. When implemented properly, lean can result in significant increases in productivity, cycle time, efficiency, material prices, and scrap, which lowers costs and boosts competitiveness. Don’t forget that lean isn’t just for the industrial industry. It can enhance team collaboration, inventory control, and even customer service.
Organisations are continuously looking for methods to streamline processes, save waste, and boost overall efficiency in the fast-paced, cutthroat business world of today. Lean Management is one approach that has found a lot of success in helping to realise these objectives. Toyota invented lean principles, and they have now spread outside the manufacturing business to be used in a variety of industries, such as technology, finance, and healthcare. We’ll explore the major Lean principles in this blog and show how leaders can use them to promote success and continuous improvement in their organisations.
Leader’s Tip:
Strive to deliver products or services to customers just when they need them, minimizing inventory and waste.
Key Lean Principles
Lean manufacturing principles were created by Toyota and have since been used in a variety of industries to increase productivity, cut waste, and boost overall performance. Let’s delve deeper into these essential Lean principles:
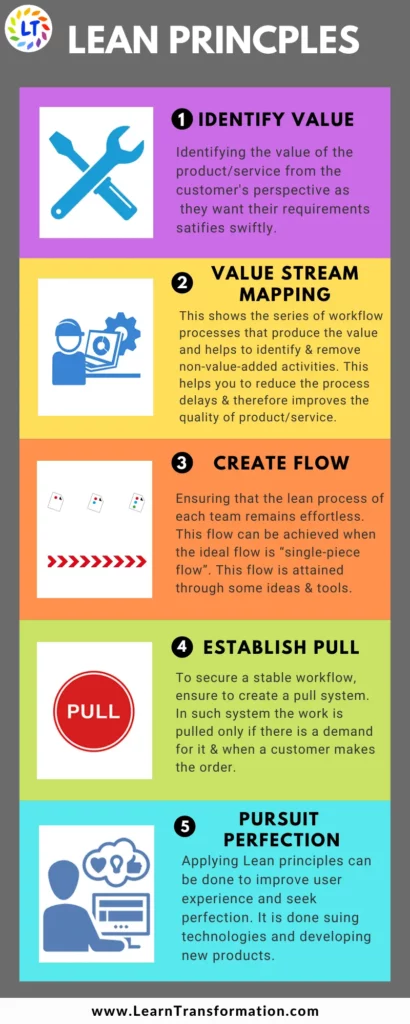
- Focus on Value-Added: Lean starts with determining what provides value in the eyes of the customer. This principle places a strong emphasis on comprehending consumer requirements and expectations to make sure that goods and services are in line with what clients really value.
- VSM: Value Stream Mapping:Value stream mapping, a visual tool, improves information and material flow analysis and enhancement within a process. It aids in locating wasteful regions, clogs, and areas where advancement is possible.
- Flow: The goal of the flow principle is to make sure that work proceeds constantly and seamlessly through processes. To optimise workflow, it entails reducing batch sizes, getting rid of delays, and minimising interruptions.
- Draw Systems: Pull systems are intended to develop a workflow that is driven by demand. Work is only pulled when it is necessary, as opposed to being pushed through a process. A common pull system that aids in preventing overproduction is kanban.
- Standardisation: For uniformity and efficiency, work processes and procedures must be standardised. Organisations create and maintain standardised work instructions as a foundation for ongoing efforts at improvement.
- Kaizen: Continuous Improvement: A basic Lean principle is kaizen, which translates to “continuous improvement” in Japanese. It promotes an environment of ongoing learning and problem-solving. Teams have the authority to identify and rectify inefficiencies, no matter how minor, to drive continuous improvement.
- Respect for Individuals: Respecting and appreciating employees is a key component of the lean methodology. Leaders encourage a culture where team members are motivated to share their observations and improvement suggestions. This notion acknowledges that empowered and engaged workers are more likely to promote change.
- Visual Control: Performance dashboards, Kanban boards, and Andon systems are examples of visual management tools that make information accessible and simple to interpret. These technologies offer a visual depiction of the condition of operations at the time in order to facilitate speedy decision-making and problem-solving.
- JIT: Just-in-Time: JIT is a Lean concept that tries to reduce waste by providing the appropriate amount of resources or goods at the appropriate time. It reduces inventory levels, decreases storage expenses, and ensures that goods are manufactured or supplied only when needed.
- Reducing Waste (Muda, Mura, and Muri): Overproduction, delays, pointless transportation, surplus inventory, excessive processing, flaws, and underutilised personnel skills are just a few examples of the waste that Lean detects. The objective is to methodically locate and get rid of these waste sources.
Efficiency, quality, and customer happiness can all be significantly raised by incorporating these Lean principles into an organization’s procedures and culture. It’s crucial to remember that Lean is a constant commitment to waste reduction and improvement rather than a one-time effort. Organisations can increase their agility, responsiveness, and competitiveness in the modern, dynamic business environment by adopting these ideas.
Also Read: Digital Transformation: The Role of Effective Digital Strategies
Leader’s Tip:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement, empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste in processes.
Also read: Exclusive Lean Digital Transformation Interview with Mr. Gourav Dudeja
The importance of Lean principles
Detailing the significance of Lean principles:
- Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: Lean management practises emphasise reducing waste, streamlining procedures, and improving workflows. As a result, it increases productivity, shortens lead times, and boosts efficiency. Organisations are able to accomplish more with fewer resources because employees are able to work faster.
- Cost-saving measures: Lean principles assist businesses in making considerable cost reductions by locating and removing waste in different forms, including overproduction, excess inventory, and pointless transportation. Reduced operational costs and increased resource efficiency decrease the overall cost.
- Better Quality: The emphasis of lean principles is on creating high-quality goods or services from the beginning. Organisations can lower errors and defects, resulting in higher-quality output, through continuous improvement initiatives and standardised processes. In turn, this results in happier customers and less rework.
- Faster customer delivery: Lean’s emphasis on cutting down lead times and developing a system based on flow ensures that goods or services get to clients more promptly. For businesses to remain competitive and satisfy client demands, shorter delivery times are crucial.
- Enhanced Client Satisfaction: Understanding client demands and providing value accordingly are top priorities in lean principles. Enhancing customer happiness, fostering loyalty, and fostering long-term connections are all made possible when businesses regularly meet or surpass their customers’ expectations.
- Making better decisions: Lean promotes decision-making based on data. Key performance indicators (KPIs) enable organisations to make informed decisions, pinpoint areas for development, and modify plans as necessary.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Lean businesses respond swiftly to changing market conditions, staying competitive by adapting to shifts in demand, trends, and disruptions.
- Staff Engagement: Lean principles value employee input and participation in efforts for ongoing improvement. Engaging employees empowers them, unlocking creativity and motivation for better outcomes.
- Sustainability: By lowering waste, saving resources, and reducing environmental effect, lean principles encourage sustainable practises. Sustainability is in line with contemporary values and can provide businesses an edge
- Competitive Benefit: Lean businesses have an advantage over their rivals in the marketplace. By excelling in productivity, cost-efficiency, and quality, they lead their industry.
- Changing Cultural Landscape: In order to implement Lean concepts, an organization’s culture frequently needs to change. This fosters a culture of accountability, creativity, and continuous improvement, yielding lasting benefits.
- Long-Term Achievement: Lean is a long-term commitment to excellence rather than a quick fix. Lean organisations are better able to overcome obstacles, maintain growth, and prosper in a market that is undergoing rapid change.
In conclusion, Lean concepts are vital for boosting productivity, cutting costs, improving quality, and enhancing customer value. Organizations can secure long-term success and competitiveness through Lean methods and culture.
We promise to give you a top-notch learning experience on all transformational subjects, such as leadership transformation, business transformation, digital transformation, strategy transformation, quality transformation, operational transformation, supply chain transformation, human resources transformation, financial transformation, lean transformation, and many others.
Visit this : 31 Best Books On Time Management – An Exclusive Collection
Conclusion
The essential Lean principles are a revolutionary concept that may enable leaders and organisations to achieve excellence, not merely a set of tools and procedures. Additionally, lean principles provide a road map to increased efficiency, decreased waste, and higher quality by focusing on value, optimising processes, and developing a culture of continuous development and respect for people. Thus, organizations can apply these ideas in various industries and sectors to enhance decision-making, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction. Leaders who comprehend and uphold these concepts can help their organisations succeed in a cutthroat and constantly shifting commercial environment.
Key Takeaways
- Identify value, map the value stream, create flow, establish pull, and seek perfection.
- Lean principles drive waste reduction, process efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
- Leaders play a vital role in promoting Lean principles and empowering their teams for continuous improvement.
FAQs
What is the importance of identifying value in Lean?
Identifying value is crucial in Lean because it helps organizations focus on activities that directly contribute to meeting customer needs and expectations. By understanding what customers perceive as valuable, organizations can eliminate waste and optimize processes accordingly.
What are Lean principles?
Lean principles are a set of guiding principles that originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS) and are widely used in Lean manufacturing and Lean management. They aim to eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and optimize processes in order to create value for customers.
Must Watch :

