In today’s fast-paced, ever-changing environment, the ability to deliver value effectively and predictably is more important than ever. And the whole point of Lean is to produce value in a consistent and efficient manner.
What is Lean Transformation?
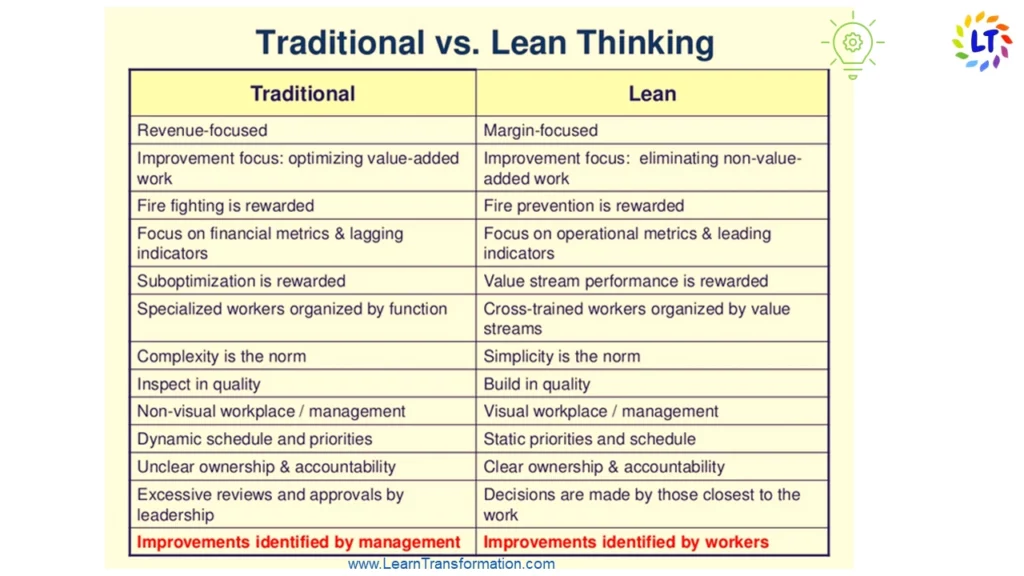
The term “lean transformation company” refers to the strategic, tactical, and operational adjustments that companies make to give more value to their customers. These developments represent a broad shift in corporate mindsets away from traditional business procedures and toward a more value-driven, streamlined approach.
Unlock a world of knowledge with just one click: Navigating Lean Digital Transformation
When it comes to Lean transformation, there is no one-size-fits-all solution: Lean starts as a grassroots movement led by a single team or department in certain firms, then spreads throughout the organisation. Others are pushing for Lean transformation from the top down, which comprises a well-thought-out, well-executed effort to adopt Lean techniques, principles, and business structures.
All Lean projects, however, have the same goal: to enable businesses to provide better value to their consumers in a sustainable manner.
Any organisation’s competitiveness, ability to adapt, and culture arise from the routines and habits which by the people in the organisation conduct themselves every day. It is an issue of human behaviour.
- What is Lean Transformation?
- What is the importance of Lean Transformation?
- What’s the Best Way to Get Started with a Lean Transformation?
- The Lean Transformation Model
- Purpose on the basis of Values
- Continuous Improvement Process
- Long-Term Capabilities Development
- Lean Management Methodology
- Mindset, Lean Thinking, and Assumptions
- Conclusion
What is the importance of Lean Transformation?
Lean transformation allows businesses to make the fundamental shift from surviving to flourishing by removing organisational structures, practises, and ways of thinking that block the efficient delivery of value.
What’s the Best Way to Get Started with a Lean Transformation?
- The first step in starting a Lean transformation is to identify the transformation’s goals:
- What are our reasons for pursuing Lean transformation?
- How are the core problems that transformation is designed to address?
- What are our short- and long-term change goals?
- Clarity and buy-in on these fundamental questions are important to the success of your Lean transformation.
Check it out – Decision Making and Problem Solving is Essential Skill for Every Leader
The Lean Transformation Model
Despite the fact that not every company approaches Lean transformation in the same way, all successful transformations have five key elements in common. The following are the details:
- A value-based objective
- The process is always being improved.
- Long-term capability development
- Lean management system
- Assumptions, attitude, and lean thinking are all things to consider.
Purpose on the basis of Values
Organizations turn to Lean because they want to be able to consistently and predictably create and deliver more value with less waste.
It’s important to define value in the Lean sense: Value, in Lean, refers to any activity, process, product, or outcome that benefits the customer.
Anything that does not provide value to the client is considered waste. This single concept should act both a catalyst and a prism through which all decisions are made during the Lean transformation.
Also Read: 31 Best Books If You Are A Health & Fitness Conscious
Leader’s Tip:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement and empowerment to encourage employees to identify and address inefficiencies.
Continuous Improvement Process
Another fundamental Lean idea is continuous improvement, or more specifically, continuous process improvement. Continuous process improvement is much more difficult to put into practice that it appears, because it demands a willingness to experiment on the side of organisations, which includes embracing failure as part of the learning process on occasion.
The (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle is commonly used in Lean enterprises to structure continuous improvement operations. The PDCA cycle, like the scientific process, comprises formulating a hypothesis, devising a strategy to test results, and lastly applying any lessons gain.
Check out this video:
Long-Term Capabilities Development
If you imagine an organisation as a human body, capability development is analogous to strength training is that it grows and maintains muscles that can be employed to meet the organisation’s demands.
Long- term capability development is encouraged in lean organisation by:
- Recruiting diverse set if individuals
- Promotions within organisation
- Education of lean is encouragable
- Providing opportunities for professional development inside the organisation
- Diverse viewpoints are encouraged, as in constructive conflict.
Low employee turnover is a sign of successful competence development.
Lean Management Methodology
Lean leadership is all about serving others. Leaders in a company’s Lean transformation and beyond have the role of uniting teams around a shared goal and then removing any obstacles that hinder them from achieving it.
Leaders are called to spend more time “in the trenches” with teams, so that they can truly understand the issues teams are facing, and add value by helping to resolve those issues.
Another crucial part of Lean Culture is a commitment to making data-driven decisions: opinion must give to reality in order to continuously improve and produce actual value. Lean leaders are responsible for promoting a scientific, data-driven approach to work.
Leader’s Tip:
Embrace data-driven decision-making, eliminate waste, and optimize processes to streamline operations effectively.
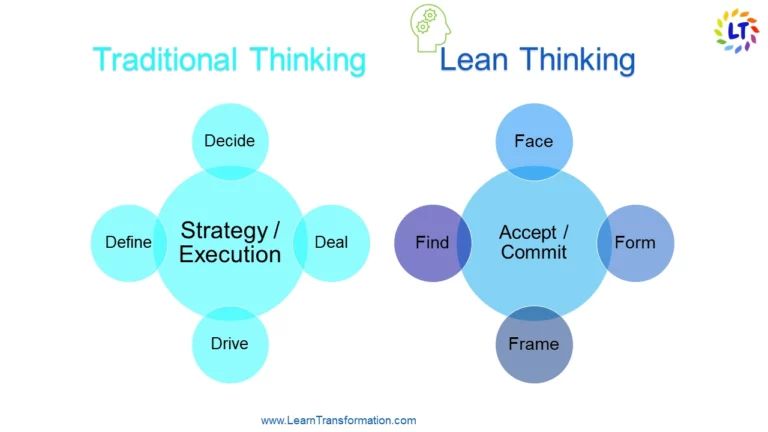
Mindset, Lean Thinking, and Assumptions
Finally, a successful Lean transformation demands a shift in mentality, assumptions, and thinking, all of which contribute to company culture.
Changing the culture of any organization is difficult, and does not happen overnight.
Some of the major cultural adjustments that must occur in order to implement a Lean Transformation are as follows
- Embracing the Lean philosophy on a personal level
- Prioritizing the creation of value over the pursuit of profit
- Accepting failure and experimenting; valuing learning above “wins”
- Embracing a data-driven decision-making approach
- The voices around the company has been in notice
- Changing the leadership role; rejecting the premise that the best ideas come from the highest paid- personnel
- Transparency and accountability are praised, while “politics” is frowned upon.
Check it out – Transformational Leader Should Avoid these 10 Habits to be Successful
Conclusion
Globally employ lean techniques and practices in a variety of industries, and the lean idea has a demonstrated track record of continuous improvement. For firms, becoming a lean enterprise has resulted in remarkable success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lean transformation Model?
The Lean transformation model is a straightforward but comprehensive approach to launching and implementing a change endeavour. It’s simple to remember and even simpler to teach, especially to folks who are new to Lean.
What is a PDCA cycle?
The (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle is commonly used in Lean enterprises to structure continuous improvement operations. The PDCA cycle, like the scientific process, comprises formulating a hypothesis, devising a strategy to test results, and lastly applying any lessons gain.
Key Takeaways
- Prioritize employee involvement and empowerment for sustained Lean transformation.
- Emphasize data-driven optimization and waste reduction to enhance company efficiency.
- Cultivate adaptability and responsiveness to thrive in a dynamic business landscape.