When I was young I used to think that money was the most important thing in life and now that I am old, I know it is.
Oscar Wilde
Exploring 5 New Trends in Financial Services: What You Need to Know
For too long, banks and alternative institution (FI) organizations have struggled to stay up with the buyer promoting and flexibility of loyalty enablement relative to alternative industries. This year, however, can see a huge shift in how banks build out their client growth and retention ways through customized client journeys and experiences. Financial Services in the VUCA World was outlined by an unexpected acceleration in digitization and digital engagement—pushed by the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Transformation close up their commerce floors and touch to remote commerce, mobile banking transactions spiked, personal commerce apps saw record group action volumes, and center personnel unbroken client support going by functioning from their living rooms.
Also check: 31 Best Award Winning & Nominated Books – An Exclusive Collection
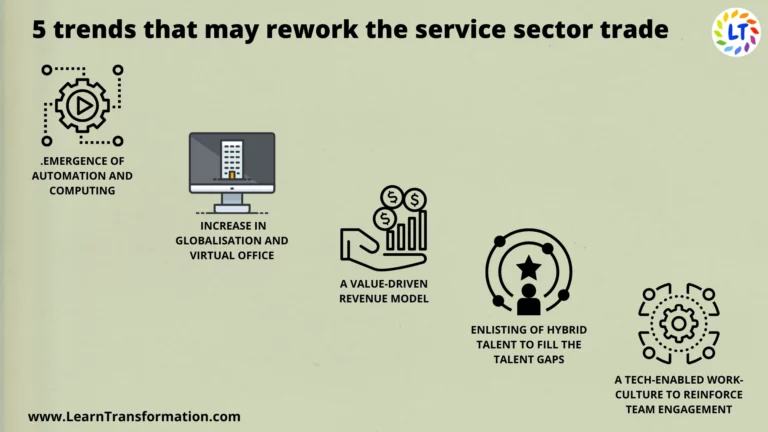
5 New Trends That May Reword The Financial Services Sector

So, Here are the highest five trends we tend to see happening within the money services businesses in the VUCA environment.
1. Hyper-Personalization-
New generation can become thought customers of banks. This rising generation of shoppers expect to be treated as people and not as segments, which implies banks have to incorporate a way stronger kind of personalization – what we tend to term hyper-personalization.
This personalization may take the shape of permitting the client to style their own suite of banking merchandise supporting their circumstance, desires and preferences to pick specific advantages they want to receive from a broad choice of banking options and advantages.
[TIP : Because the coronavirus crisis catalysis a shift towards contactless services, touch-based bioscience can seemingly lessen and become less common.]
2. “Whole-of-Bank” Loyalty-
Banks face the challenge of treating client loyalty as a {part of} an overall relationship with the bank and not as part of one product feature (e.g. credit cards). This relationship extends well on the far side of a mastercard and will embody all merchandise and services that a client consumes, whether or not from the retail bank, the business bank or a wealth product like insurance or investment merchandise.
Consider this within the context of Apple, that has been ready to cement whole loyalty by providing glorious merchandise and client service across the complete relationship.
3. Digital Transformation-
The money services business is witnessing a continued and aggressive concentrate on digitization. And it is also the adoption of latest and rising technologies to usher in operational efficiencies, enhance speed-to-market and deliver superior client experiences. Banks square measure scaling down outlay on branches to speculate in self-service digital channels. Because mobile and on-line banking become additional widespread among customers.
[TIP : By exploiting huge information as the simplest way of watching customers’ usual outlay habits, it’s way easier for money and blockchain service suppliers to identify something suspicious.]
4. Collaboration with Fintechs-
Banks’ bequest systems square measure their biggest barrier to growth and technological innovation. As a result, several banks square measure partnering with FinTech corporations to create their digital expertise.
Today, however, bank/Fintech partnerships square measure more and more the norm, with the latter providing promoting, administration, loan conjugation or alternative services enabling banks to supply tech-enabled banking merchandise, options and advantages. As a result, these partnerships square measure starting to re-shape the money services landscape.
Also Read: Innovation Transformation- Types And Best Examples
5. Artificial intelligence and AI-
Whereas client desires and competitive forces demand that banks adopt full-fledged digitization, performance pressures compel lenders to cut back prices and keep in operation margins healthy.
As new restrictive necessities and information protection. laws place further strains on already-stretched resources, rising technologies like AI and Artificial Intelligence square measure serving to banks address these constraints with efficiency. In fact, several pioneering corporations within the FS business square measure are already experimenting with multiple use cases of AI in their operations.
[TIP : Responding to a recent client shift towards things like Amazon’s Alexa and alternative voice assistants, banks have found new ways in which to boost client service exploitation AI-drive voice technology]
Also See: 5 Challenges and Role of a Good Leader
Leader’s Tip:
Adopt new technologies to improve financial services’ effectiveness and user experience.
Check out the Video-
What is VUCA in financial industry?
VUCA is an acronym that stands for Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity. It is a term used to describe the current business environment. Particularly in the financial industry, which is characterized by rapid change, increasing complexity, and heightened uncertainty. Here are some key points about VUCA in the financial industry:
- Volatility: Refers to the rate and magnitude of change in the financial markets, including stock prices, interest rates, and currency values. Volatility can be caused by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical events, and market speculation.
- Uncertainty: Refers to the lack of predictability and clarity in the financial markets, as well as the wider business environment. Uncertainty can be caused by a variety of factors, including regulatory changes, trade policy, and technological disruption.
- Complexity: Refers to the interconnectedness of financial markets and the increasing complexity of financial instruments and products. Complexity can make it difficult for financial institutions to understand and manage risks effectively.
- Ambiguity: Refers to the lack of clarity and the presence of multiple, conflicting interpretations in the financial industry. Ambiguity can be caused by a variety of factors, including regulatory guidance, legal requirements, and ethical considerations.
Overall, VUCA in the financial industry represents a significant challenge for financial institutions. And it requires them to be agile, adaptable, and innovative in order to survive and thrive in this rapidly changing environment.
Financial institutions must be able to anticipate and respond to changes in the market. While also managing risk effectively and maintaining the trust of their customers and stakeholders. Hence, By embracing VUCA and developing strategies to address these challenges. Financial institutions can position themselves for long-term success in the digital age.
Major challenges of Financial Services in the VUCA World
The VUCA world presents several challenges for the financial services industry. So, Here are some of the major challenges:
1. Volatility: The financial industry is particularly sensitive to market volatility, and the VUCA world has made it increasingly difficult to predict and manage risks. Financial institutions need to be able to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and respond to sudden shifts in investor sentiment.
2. Uncertainty: The VUCA world is characterized by significant uncertainty, particularly around regulatory changes and geopolitical events. Financial institutions need to be able to navigate these uncertainties while maintaining stability and ensuring compliance with regulations.
3. Complexity: The financial industry is becoming increasingly complex, with new products and services emerging all the time. Financial institutions need to be able to understand and manage these complexities, particularly around risk management and compliance.
4. Ambiguity: The VUCA world is also characterized by ambiguity, with multiple interpretations of regulations and market conditions. Financial institutions need to be able to navigate these ambiguities while maintaining trust with their customers and stakeholders.
5. Technology: Technology is transforming the financial industry. But, it also presents challenges around cyber-security, data privacy, and the management of new technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence.
Overall, the VUCA world presents significant challenges for the financial services industry. And financial institutions need to be able to navigate these challenges while maintaining stability, managing risks, and delivering value to their customers.
This requires agility, innovation, and a willingness to adapt to changing conditions in the marketplace. Financial institutions that are able to meet these challenges head-on will be well-positioned to succeed in the VUCA world.
What are VUCA factors examples in financial services?
The VUCA factors – volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity – are particularly relevant to the financial services industry, which operates in a constantly changing and unpredictable environment. Here are some examples of how these factors manifest in financial services:
- Volatility: Financial markets are inherently volatile, with prices constantly fluctuating in response to economic, political, and other factors. Financial institutions need to be able to manage this volatility, including the risk of sudden market crashes and the impact of external events such as natural disasters or cyber attacks.
- Uncertainty: The financial industry operates in a highly regulated environment, with rules and regulations that are constantly changing. Financial institutions need to be able to navigate this uncertainty while maintaining compliance with regulations and managing risks effectively.
- Complexity: Financial services are becoming increasingly complex, with new financial products and services emerging all the time. Financial institutions need to be able to understand and manage this complexity, including the risks associated with new products such as cryptocurrencies and derivatives.
- Ambiguity: Financial markets are often subject to ambiguity, with multiple interpretations of market conditions and regulations. Financial institutions need to be able to navigate these ambiguities while maintaining trust with their customers and stakeholders.
- Technology: Technology is transforming the financial services industry, with new technologies. Such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics presenting both opportunities and challenges. Financial institutions need to be able to manage the risks associated with new technologies. While leveraging them to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
Leader’s Tip:
To ensure business viability and customer trust, stay informed about regulatory changes and compliance needs.
Conclusion
From money services establishments to vendors, regulators, and supervisors, this VUCA environment is probably going to be an era of deliberate cultural transformation to search out new ways in which to operate along to form safer, cheaper, additional comprehensive, and additional evenhanded money markets.
This year at Google Cloud, we’ll continue operating with our customers across money services to assist them. To steel themselves for the long run, through our technology, tools, and innovation partnerships.
FAQ :
What is the financial industry?
The financial industry includes a range of businesses and institutions that provide financial services to individuals, businesses, and governments. This includes banks, insurance companies, investment firms, and other financial intermediaries.
What services are provided by the financial industry?
The financial industry provides a wide range of services, including banking, insurance, investment management, securities trading, and financial advice.
What is the role of regulation in the financial industry?
Regulation plays a critical role in the financial industry, helping to ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system. Regulatory bodies oversee the industry to ensure that financial institutions comply with laws and regulations, maintain adequate capital reserves, and manage risks effectively.
How has technology impacted the financial industry?
Technology has had a significant impact on the financial industry, enabling the development of new products and services, improving operational efficiency, and expanding access to financial services. This includes the rise of online banking, mobile payments, robo-advisors, and blockchain technology.
Key Takeaways:
- Financial services are changing as a result of digital transformation, which is also fostering innovation and enhancing accessibility.
- Intelligent decision-making, risk management, and individualised financial solutions are made possible by utilising AI and machine learning.
- Blockchain technology transforms procedures like payments and identity verification by enabling secure, transparent transaction