Blockchain is the biggest opportunity set we can think of over the next decade or so.
Bob Greifeld
The Power of Blockchain: Unlocking Its Potential for Business Transformation
Blockchain is a shared, unchangeable ledger that eases the process of maintaining transactions & stalking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (a car, a house, cash) or intangible (patents, intellectual property, copyrights). On a blockchain network, all involved can decrease risk and also reduce costs by tracking practically anything of value.
Satoshi Nakamoto introduced this concept in 2008.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed database that maintains a list of ordered records, called blocks. Blockchain refers to the binding together of secure blocks of data in chains using cryptographic principles. Every block has a timestamp & a link to a previous block. A group of computers called nodes manages the unchangeable ledger of data, not a single authority. It ensures that no single entity controls the flow of information or transactions. Users can only edit the information of the block-chain that they “own” by having the private keys mandatory to make changes to the file. Cryptography makes sure that everyone’s copy of the distributed block-chain stayed in synch.
This enables a verifiable & decentralized record of transactions between two people. Everyone can send value anywhere in the world where they can access the blockchain file. This makes blockchain technology a protected channel for information flow.
4 Key enterprise Blockchain Use-cases:
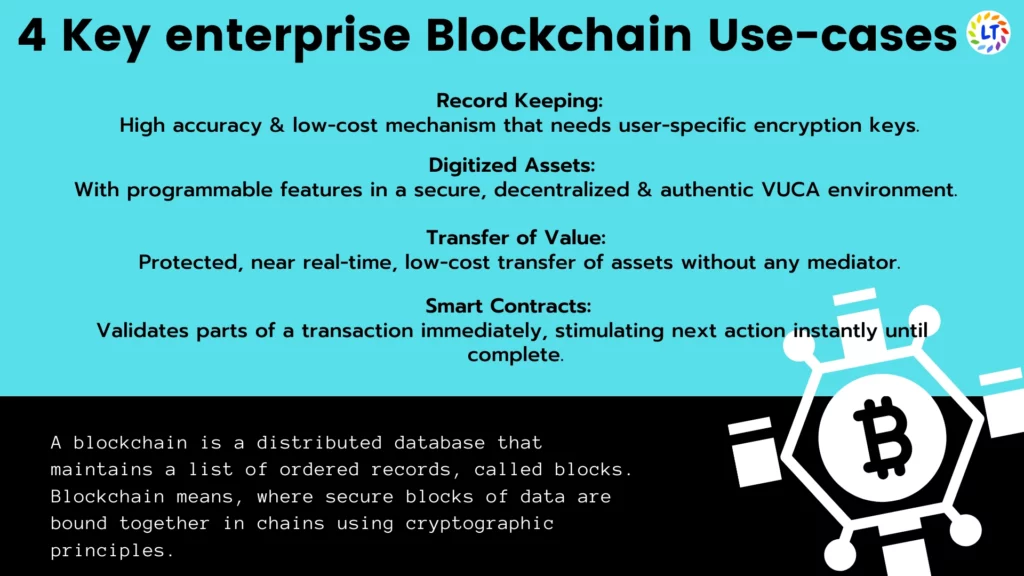
Record Keeping: High accuracy & low-cost mechanism that needs user-specific encryption keys.
Digitized Assets: With programmable features in a secure, decentralized & authentic VUCA environment.
Transfer of Value: Protected, near real-time, low-cost transfer of assets without any mediator.
Smart Contracts: Validates parts of a transaction immediately, stimulating next action instantly until complete.
Enterprise blockchain aims to settle business issues related to multi-enterprise interactions & eases the creation of new business models through the application of distributed ledger technologies.
Also Read: Best Books
How does Blockchain Work?
As on the internet, anyone can publish information & then others can retrieve it anywhere in the world. You can transfer the value of whatever is store in that section of the blockchain management if you use your private key and someone else’s public key. But you need to possess a private, cryptographically generated key to edit only the blocks you possess.
Blockchain refers to the binding together of secure blocks of data in chains using cryptographic principles.
So, to use the Bitcoin example, users transfer blocks using keys, which hold units of currency that have financial value. So, Banks commonly perform the function of recording the transfer.
It also does a second role, in establishing trust & identity, because no one can edit a blockchain without having the corresponding keys. The network rejects edits that are not verified by those keys. The keys, like physical currency — could subjectively be stolen. But, we can keep a few lines of computer code secure at a low cost.
This means that the vital functions supported by banks — confirming identities to stop fraud & then recording authorized transactions — can be carried out by a blockchain more swiftly & precisely.
Leader’s Tip:
Foster an innovative, collaborative, and experimental culture to study blockchain’s potential to alter industries.
Why is Blockchain Important?
1. Unmatched Security-
- Transaction verification is one of the basic features of blockchain technology.
- A transaction must be requested through a wallet & sent to all the computers in a blockchain network. Each of these nodes or computers must verify the transaction against a set of fixed rules in that network. Then, we place the information in a block and encrypt it with a hash. Once this hash is verified by the nodes, the information stored in that block is permanent, immutable & secure. Any changes to the data by hackers finally alter the hash & the entire chain of transactions linked to the hash. So, Anyone cannot alter or misuse the information.
2. Increased Cost & Time Efficiencies-
- It eliminates the need for third-party mediation. Instead of relying on third-party mediators for verification & the movement of information, blockchain uses cryptology to enable direct transactions between two parties.
- It also eliminates the time-consuming process of hitting on the doors of central authorities.
- Maintaining the record through a single ledger also eliminates the litter of error-prone manual processes, therefore saving time & money.
3. Finer Transparency-
- Being a type of distributed ledger. The nature of blockchain technology allows alterations to make only through the agreement of all network participants who share the same documentation. Even a single modification in the transaction record would mean that all following records will have to update.
- It means everyone is aware of any change. Further, This makes sure transparency & places a high level of accountability for everyone who handles the document. The transaction history also gives an audit trail of where the information originated from. And every instance of when transactions happened & changes were made. This helps in ensuring the originality of the assets as well as prevention of fraud.
Private vs. Public Blockchains
1. Public or Permissionless Blockchain:
As a peer-to-peer network, integrated with a distributed time-stamping server. Public blockchain project records can maintain free, to interchange information between parties. Hence, There’s no requirement for a managing director. In effect, the block-chain users are the managing director. Furthermore, Permissionless blockchains start with a pool of cryptocurrency to pay miners or service providers to participate in the process.
2. Private or Permissioned Blockchain:
It permits companies to generate & centrally administer their transactional networks that can be used inter- as well as intra-company with partners.
Also, block-chain networks can be used for “smart contracts,” or scripts for business automation that accomplish when certain legitimate conditions are met. For example, after a bad batch of lettuce resulted in consumers getting sick from e-coli, IBM & Walmart generated a blockchain based supply chain to track produce from farm to table. Moreover, Walmart has demanded its produce suppliers enter their data into the block-chain database. Once on the block-chain implementation, production can be automatically tracked through smart contracts from point to point, eliminating human intervention & error.
De Beers, which sways about 35% of the world’s diamond production, has also started a blockchain-based supply chain to track diamonds for authenticity & to make sure they aren’t coming from war-torn regions where miners are exploited. After driving a blockchain-based produce supply chain tracking system, Walmart is telling suppliers to get their product data into the system so they can start tracking produce from farm to store.
Final Word
At last, Blockchain technology has the power to affect all recordkeeping processes, including the way transactions are initiated, authorized, processed, recorded & reported. According to a Global block-chain projects survey done by Deloitte: It declares that such increased production is here to reside, with 39% of global respondents saying they have already included blockchain into production (41% of respondents from companies with greater than US$100 million in revenue), a significant increase from 23% last year. So,That’s the central takeaway from their 2020 Global Block-chain Survey, which discovers that leaders no longer consider the technology revolutionary & solely promising—they now see it as essential to organizational innovation.
In 2020, a progressive number of leaders have expressed this sentiment, saying that they see blockchain as a top 5 strategic priority, and are increasing their investments in staffing & block-chain technologies.
Leader’s Tip:
Be a strong leader in managing regulatory obstacles, resolving privacy issues, and advancing the moral use of blockchain technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of cryptography in blockchain?
Cryptography ensures the security and privacy of transactions on the blockchain by encrypting data, creating digital signatures, and verifying the integrity of the information.
How does blockchain ensure trust and transparency?
Blockchain ensures trust and transparency by storing a complete and unchangeable record of transactions that can be verified by all participants in the network.
Key Takeaways:
- Blockchain revolutionises sectors including finance, supply chain, and healthcare with increased security, transparency, and efficiency.
- Successful blockchain deployment, partnership development, and adoption through education and awareness are all dependent on effective leadership.
- Understanding the technical details of blockchain, looking into interoperability options, and keeping up with changing standards and laws are all necessary for adoption.